Webhook notifications
Last updated: Mar-04-2026
Cloudinary provides a webhook notification feature for informing your backend about certain actions that have been completed, either via API method call or via user action within the Console UI. When the action is completed, an HTTP POST request is sent to a public notification URL you provide. The payload contains all the results pertinent to that particular action.
You can use webhook notifications to:
- Handle asynchronous calls. By default, Cloudinary's upload API works synchronously. For example, uploaded assets are processed and eager transformations are generated synchronously during an upload API call, which means that the original asset and derived assets are available immediately for delivery and further management. However, in some cases you may need to be notified that an upload has completed, or you may want to process actions asynchronously in the background, especially actions that require a relatively long time to process and require your users to actively wait for the processing to finish.
- Keep aligned when other users in the system make changes. It's important to listen for changes made in your system and update accordingly to make sure there aren't any inconsistencies. You can set up code that listens for notifications, and then uses the data to make automatic updates. For example, you can set up a webhook to receive notifications when assets are renamed, and then trigger a search and replace to update the asset name anywhere it exists.
-
Integrate Cloudinary with other platforms. If you're using Cloudinary assets from within a different platform, listen for changes being made to assets in Cloudinary in order to keep synced. For example, you can set up a structured metadata field to indicate whether assets should be published or unpublished. When you receive a notification within the other platform indicating that this metadata field was changed, trigger the appropriate action in your code.
For more information about how to integrate Cloudinary with another platform, see How to build your own integration.
-
Trigger another operation. If an action must follow a specific event, you can listen for that event and use it to trigger the action. For example, use the notification that an asset has been uploaded to trigger adding the asset to your catalog, or for user-generated content to handle the result of a moderation check, determining if it's safe to display the image or video.
Examples- The Cloudinary Solutions team took advantage of this option to create an open-source library that can learn and then auto-tag faces with names using an Amazon Rekognition lambda function that's triggered by the notification following the upload of a photo to a dedicated 'training' folder in Cloudinary.
- The profile picture sample project demonstrates a UGC use-case showing images moderated on upload and the use of Cloudinary webhooks to check the moderation results.
- The video review sample project demonstrates a UGC use-case showing videos moderated on upload, the generation of eager transformations, and the use of Cloudinary webhooks to wait for the moderation, eager, auto chaptering and auto transcript notifications. The frontend waits for successful notifications before displaying the video.
Global notification URLs
You can set one or more global notification URLs in the Webhook Notifications page of the Console Settings or programmatically using the triggers method of the Admin API.
Once you've set up either a single or multiple notification URL(s), Cloudinary automatically sends responses to the appropriate URL address(es) any time a relevant action in the Console UI is performed or a call to a relevant Cloudinary API method is made.
If you're using a single notification URL, configure it to receive all notifications.
However, adding multiple notification URLs enables you to specify which destination receives notifications for each type of action. This level of control makes is easy to trigger flows or sync multiple parts of your ecosystem when integrating Cloudinary with other platforms. It also allows you to:
- Dedicate a separate notification URL to handle actions relevant to each of your workflows.
- Organize your destinations according to their purpose.
- Spread out the traffic among several endpoints to avoid performance issues.
Tips and considerations for adding multiple notification URLs
- Make sure you assign every notification type that you listen for in your code to at least one notification URL.
- You can optionally set one notification URL to receive all responses as backup.
- Each notification URL can handle several event types, and conversely the responses for a single notification type can be sent to several notification URLs.
Managing global notification URLs
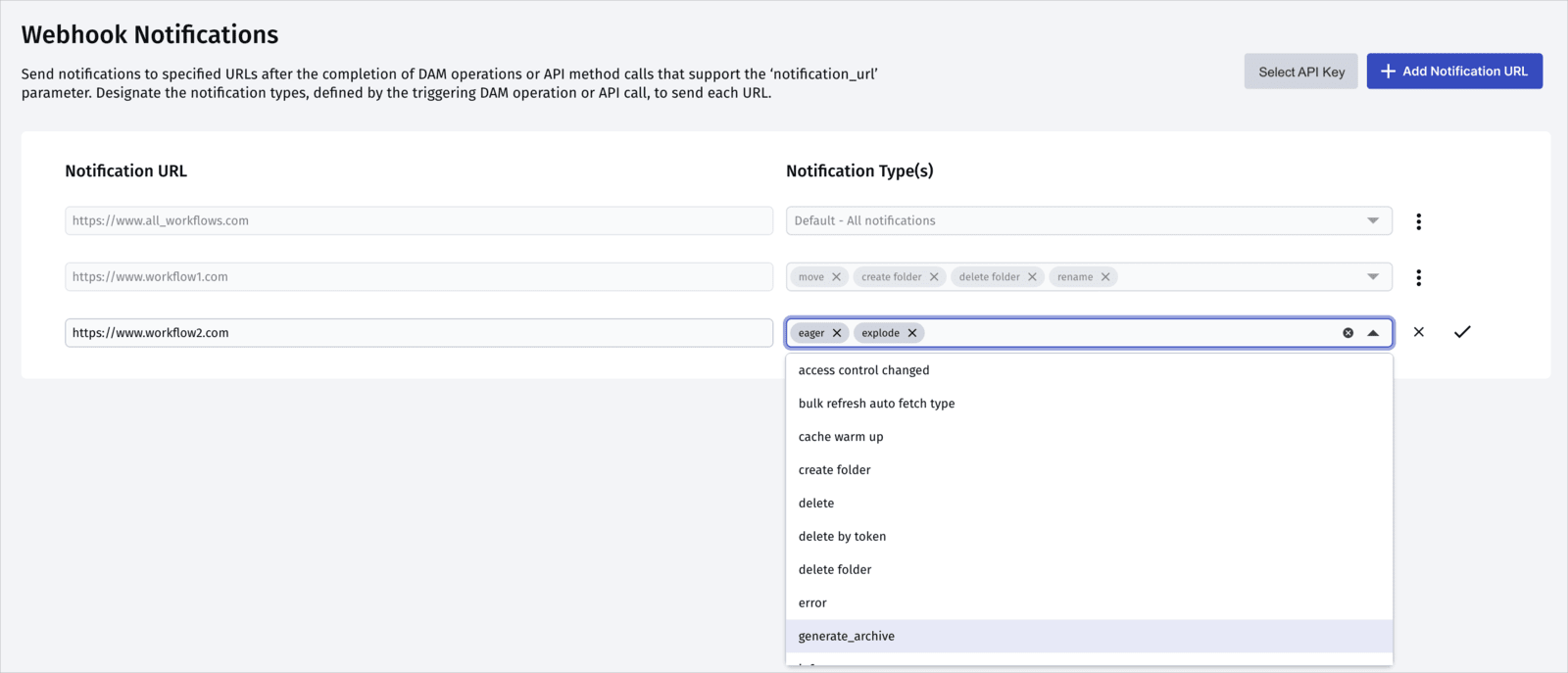
You can manage webhook notifications either from the Webhook Notifications page of the Console or using the triggers method of the Admin API. You can configure up to 10 notification URLs per product environment.
In the Console, each notification URL is linked to all configured Notification Types (triggering events). However, when programmatically managing webhook notifications, you're working with a trigger — a single triggering event paired with a single notification URL. As a result, programmatically creating a trigger reflects in the Console by either generating a new notification URL with a single Notification Type or appending a new Notification Type to an existing URL's list of notifications.
Managing webhook notifications from the Console
To manage multiple notification URLs via the Cloudinary Console, go to the Webhook Notifications Console Settings page.
By default, when you add a new notification URL, the Default - All notifications option is selected as the default type. If you're using a single notification URL, or want to use one of your notification URLs as backup for all events, keep that default behavior.
You can also (or alternatively) add different Notification URLs, and specify the Console UI action and/or API method Notification types you'd like to receive notification about at each URL. You can configure up to 30 notification URLs per product environment.
In addition, you can select the API key for verifying all your notification signatures. For more information, see Dedicated API key for webhook notifications.
notification_type key that's returned in the notification response. Managing webhook notifications programmatically
To manage notification URLs programmatically, use the triggers method of the Admin API. Each trigger denotes a unique event type linked to its notification URL. Your product environment supports triggers up to a maximum determined by multiplying the number of unique event types by the limit of 30 notification URLs.
When an event of the specified type occurs, a response is sent to its corresponding notification URL.
For example, set up the https://mysite.example.com/my_notification_endpoint URL to receive a notification whenever an upload is completed:
- If you want a trigger to receive all notifications, set its
event_typetoall. - The
event_typevalues correspond with thenotification_typekey that's returned in the body of the notification response. For a full list, see Event types. - A dedicated API key for verifying all webhook notifications can be set programmatically via the PUT method of the Provisioning API access key endpoint, available for Enterprise customers upon request.
API method call notifications
When you call certain API methods, a response is sent to the notification URL you configured to listen for that action upon its completion.
For a full list of possible triggering actions see this table.
For some examples of notification responses from these types of actions, see the Notification response examples section.
Console UI notifications
When a user performs any of the following actions in the Console UI, a response will be sent to the notification URL you configured to listen for that action upon its completion.
- Uploading a new asset.
- Renaming the asset's public ID.
- Deleting an asset. Deleting a folder that contains assets will also trigger a delete notification for all individual assets in that folder. Note that deleting empty folders does not send a notification.
- Updating an asset's display name. (Not relevant for product environments using the legacy fixed folder mode.)
- Moving an asset between folders changes the
asset_foldervalue, and triggers a move notification.- In the legacy fixed folder mode, moving an asset to another folder in the Media Library changes the
public_idvalue, and thus triggers a rename notification.
- In the legacy fixed folder mode, moving an asset to another folder in the Media Library changes the
- Adding, removing or updating the contextual metadata for an asset.
- Adding, removing or updating the structured metadata for an asset.
- Adding or removing a tag for an asset.
- Adding or removing related assets relationships.
- Updating the access control setting for an asset.
- Creating a new asset folder.
- Deleting an asset folder.
- Restoring a previous asset version.
- Making a decision that changes the status of the proof during proof review in one of the stages of the creative approval flow.
For a full list of possible triggering actions see this table.
For some examples of notification responses from these types of operations, see the Notification response examples section.
Notification Payload
When an action that triggers a notification is completed, an HTTP POST request will be sent to the notification URL you provided. The post data will contain all the result details for the action that triggered it. The body of this POST request is essentially the same information as you get in response to a standard synchronous request.
Here's an example POST request sent by Cloudinary after an upload completes:
Cloudinary signs all notification responses, allowing you to validate that they were not sent by a third-party. The notification includes both an X-Cld-Signature header and a X-Cld-Timestamp header for validating the notification response. For more details, see Verifying notification signatures.
For additional examples of notification responses from various API calls, see notification response examples.
Notification URLs for specific API calls
In specific situations, you may want to notify your backend as soon as a method call is complete, for example when dealing with user initiated uploads from a browser or mobile device. You can tell Cloudinary to notify your application as soon as the method is complete by adding the notification_url parameter to the method call and setting it to any valid HTTP or HTTPS URL.
The following upload API methods support the notification_url parameter: upload, explicit, explode, generate_archive, and multi.
create_collage method will be deprecated as of September 16, 2025, and will no longer function after that date. Be sure to remove these features from any production code.You can continue creating collages using overlays.
For example, to add a notification_url to a specific upload call:
notification_url parameter in addition to any of the global notification URLs set to handle the relevant Notification type.Eager transformation notifications
You can instruct Cloudinary to send a separate notification whenever a requested Eager transformation completes by adding the eager_notification_url parameter to the method call and setting it to any valid HTTP or HTTPS webhook URL. Eager transformations should be set up to work asynchronously in the background after an upload completes by also including the eager_async parameter (for more details, see Eager asynchronous transformations). This eager notification is in addition to any notification sent via the optional notification_url parameter.
The following upload API methods support the eager_notification_url parameter: upload and explicit.
For example, the following method will upload the sample.jpg image and then eagerly generate two transformed images:
- Pad to a width and height of 300 pixels.
- Crop to a width of 160 pixels and a height of 100 pixels.
Furthermore, the transformations will be performed asynchronously after the image finishes uploading, with a callback URL to notify your application once the upload is complete, and a different callback URL to notify your application once the eager transformations are complete:
Notification combinations with eager
The following table shows the results of adding different notification parameters when also requesting eager transformations with and without, the eager_async parameter.
| Parameters | Result |
|---|---|
eager andnotification_url
|
The upload method response and the notification_url are sent after BOTH the upload completes and the eager transformations have finished. |
eager andeager_notification_url
|
The upload method response and the eager_notification_url are sent after BOTH the upload completes and the eager transformations have finished. |
eager andeager_notification_url andeager_async
|
- The upload method response is sent after the upload completes and include a batch_id for tracking the eager job. - eager_notification_url is sent after the eager transformations have finished with a batch_id for tracking. |
eager andnotification_url andeager_notification_url
|
The upload method response and the notification_url are sent after BOTH the upload completes and the eager transformations have finished. The eager notification is ignored. |
eager andnotification_url andeager_notification_url andeager_async
|
- The upload method response and the notification_url are sent after the upload completes and include a batch_id for tracking the eager job.- eager_notification_url is sent after the eager transformations have finished with a batch_id for tracking. |
Eager notification response
When the eager transformations are completed, an HTTP POST request will be sent to the eager notification URL you provided with details about the requested eager transformations including the HTTP and HTTPS URLs for accessing the derived images. For example:
Cloudinary signs all notification responses, allowing you to validate that they were not sent by a third-party. The notification includes both an X-Cld-Signature header and a X-Cld-Timestamp header for validating the notification response. For more details, see Verifying notification signatures.
If the eager transformation is not generated for some reason then the notification response will include a status: failed and the reason, for example:
Notification response examples
This section provides several examples of notification responses to a variety of different API calls or Media Library operations. Keep in mind that this list is not comprehensive, and that the exact content of the response will depend on the options sent with the relevant API call or the exact operation performed in the Media Library.
notification_context with information on the time the original request was triggered and the source of that request - either an email address for a UI initiated request, or the api_key of an API method call.Tags
Context
Metadata
No previous metadata
With previous metadata
Rename
(Change the public ID)
Change display name
Not supported for product environments using the legacy fixed folder mode.
Create asset folder
Move between asset folders
Not supported for product environments using the legacy fixed folder mode.
Move an asset folder
Not supported for product environments using the legacy fixed folder mode.
Delete an asset
Delete an asset folder
Not supported for product environments using the legacy fixed folder mode.
Multi generation
Proof status changed
When the status of a creative approval proof reaches a decision (for example, when a proof is approved or requires changes), a notification is sent with details about the proof and its new status.
Explode
When you include a notification_url, Cloudinary sends a single notification_type: "explode" notification when all derived assets have been generated, rather than one notification per derived asset.
Upload (simple)
Upload (complex)
Access control
Related assets
Add related assets
asset_id is the primary asset to which you added or removed relationships. The webhook notification payload doesn't include the full list of related assets. To retrieve the full list of related assets, use either:
- The response from the original Add related assets by public ID or Add related assets by asset ID API call that triggered the notification
- The Get details of a single resource by public ID or Get details of a single resource by asset ID endpoints with the
relatedparameter set totrue
Delete related assets
Image inserted from Media Library widget
asset_folder and display_name keys are also not included in the response, and the folder key is.Retry policy
In the event of a failed notification URL, the HTTP response code is assessed. If the response is not 200 OK, three additional notification attempts are initiated:
- A retry after 3 minutes.
- A second attempt after 6 minutes.
- A final retry after 9 minutes.
Troubleshooting
Understanding how to troubleshoot notification failures and identify why notifications may not reach their destination URL is essential for seamless operation. Here, we explore common failure causes and ways to avoid potential pitfalls when working with Cloudinary webhook notifications.
Common causes of failure
Payload corruption: Payload validation in webhook notifications checks if the data meets expected formatting and matches system requirements. Failure may signal data corruption issues that affect processing.
Invalid signature: Verification of the signature may fail, resulting in webhook failures.
Disabled API key: Using a disabled API key for signing the API can impact webhook functionality. To activate your API keys, go to the API Keys page of your Console Settings.
Invalid Webhook URL: A webhook was configured with an incorrect or inaccessible notification URL. For example, you may have configured an endpoint that no longer exists, or changes in the URL path may not be updated in the configuration.
Connection Timeout: Timeout errors may occur if your server experiences delays exceeding our 20-second limit. Retries happen for transient issues, but consistent server slowness may lead to notification failures.
Ways to avoid potential pitfalls
While setting up and maintaining your webhooks, keep the following potential pitfalls in mind:
Check the signature calculation: Make sure your signature calculation is accurate. This is crucial for webhook success.
Ensure JSON payload is stringified correctly: JSON payload stringifying can encounter problems like data loss, invalid JSON, and character encoding mismatches. These issues can be avoided by using standard libraries, validating JSON data, and handling special characters correctly.
Standardize hash methods: When different cloud platforms use different methods for securing webhook data, it can cause signature mismatches, leading to webhook failure. Avoid this by standardizing the hash algorithm or implementing flexible signature verification.
Avoid notification overload: Ensure your server can handle the volume of notifications, especially when there are numerous uploads.
Follow HTTP header specifications: Ensure HTTP headers are treated as case-insensitive according to the HTTP V2 specification.
Monitor endpoint logs: Regularly check endpoint logs for
500errors to identify issues with processing Cloudinary notifications.
 Ask AI
Ask AI